TrueK8S Part 07
Deploying LongHorn to our Kubernetes cluster
I learned a hard lesson about making good choices regarding storage for your kubernetes cluster. In early attempts at building my cluster I tried using an ‘nfs-subdir’ provider that provided pod volume storage backed by a local NFS server. This seemed easy and made good sense to me at the time. In practice, the I/O was so bad that many deployments failed due to enormous storage latency. Not only did it perform poorly, that storage provider also didn’t provide the snapshot mechanism that we’ll need for VolSync (up next). So take it from me, you need a good storage provider that provides features, flexibility, and good performance.
I chose longhorn as the storage provider for my cluster, mainly because there were plenty of examples around longhorn configuration in the TrueCharts community for me to follow. Longhorn allows us to utilize direct attached storage on our worker nodes for high performance, and also provides the volume snapshot features that we’ll need in the next post. You may remember back in part 1 of this guide, I referenced storage for our cluster members and some necessary extensions for TalosOS. If you skipped around, go back to part 1 and make sure that you have the util-linux-tools and iscsi-tools extensions configured.
Deploying LongHorn
You should know the drill by now. Here are the deployment resources. Once again we’ll create a kustomization to deploy longhorn, and then a separate one to configure it. I chose to do it this way because I want to explicitly wait for the longhorn UI to be online before trying to assign ingress to it, which can cause issues in re-deployment scenarios.
truek8s
├── infrastructure
│ ├── core
│ │ ├── longhorn
│ │ │ ├── helm-release.yaml
│ │ │ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ │ │ ├── namespace.yaml
│ │ ├── longhorn-config
│ │ ├── ingress.yaml
│ │ └── kustomization.yaml
│ └── production
│ └── longhorn.yaml
└── repos
├── longhorn.yaml
└── longhorn-config.yaml
./repos
longhorn.yaml
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: longhorn
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 2h
url: https://charts.longhorn.iokustomization.yaml
Add this new manifest to the repos kustomization.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- longhorn.yaml./infrastructure/core/longhorn
namespace.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: longhorn-system
labels:
pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce: privilegedhelm-release.yaml
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: longhorn
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
interval: 5m
releaseName: longhorn
chart:
spec:
chart: longhorn
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: longhorn
namespace: flux-system
install:
createNamespace: true
crds: CreateReplace
remediation:
retries: 3
upgrade:
crds: CreateReplace
remediation:
retries: 3
values:
defaultSettings:
# Increase to 3 for a multi-node cluster
defaultReplicaCount: 1
# Overprovisioning might be needed when using volsync
storageOverProvisioningPercentage: 100000
storageReservedPercentageForDefaultDisk: 10
# v2DataEngine: true
csi:
attacherReplicaCount: 1
provisionerReplicaCount: 1
resizerReplicaCount: 1
snapshotterReplicaCount: 1
persistence:
# Set to false to pick another CSI as default
defaultClass: true
# Increase to 3 for a multi-node cluster
defaultClassReplicaCount: 1
longhornUI:
replicas: 1./infrastructure/core/longhorn-config
ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: longhorn-nginx
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
ingressClassName: internal
rules:
- host: longhorn.${DOMAIN_0}
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: longhorn-frontend
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix- kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ingress.yaml./infrastructure/production
The order of operations here is to first install longhorn, then use separate kustomization to configure the ingress once longhorn and nginx are both configured.
/infrastructure/production/longhorn.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: longhorn
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 10m
path: infrastructure/core/longhorn
prune: true
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system/infrastructure/production/longhorn-config.yaml
Note the dependsOn configuration of this kustomization.
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: longhorn-config
namespace: flux-system
spec:
dependsOn:
- name: ingress-nginx
- name: longhorn
interval: 10m
path: infrastructure/core/longhorn-config
prune: true
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system/infrastructure/production/kustomization.yaml
And add these new manifests to the production kustomization
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- longhorn.yaml
- longhorn-config.yamlFinally, commit your changes and watch flux as it reconciles the changes.
git add -A && git commit -m "add longhorn"
git push
flux events --watchVerify longhorn
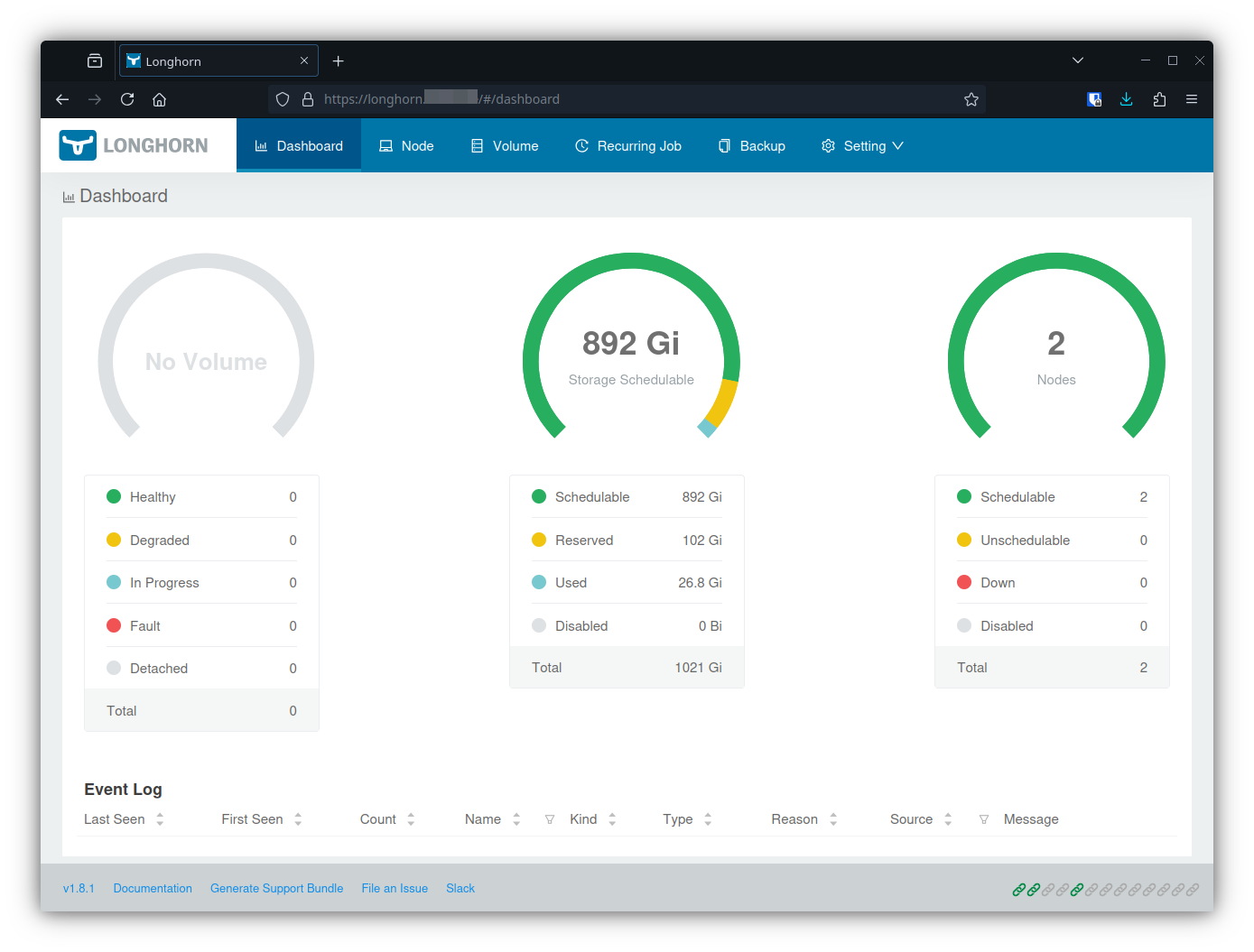
Check everything over using flux, helm, and kubectl like we did in previous steps. You should see quite a few resources created by the longhorn helm-release. You can inspect those with kubectl to understand what all it’s doing. You should also have new storage classes created by longhorn.
$ flux get hr longhorn -n longhorn-system
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
longhorn 1.9.0 False True Helm install succeeded for release longhorn-system/longhorn.v1 with chart [email protected]
$ flux tree ks longhorn
Kustomization/flux-system/longhorn
├── Namespace/longhorn-system
└── HelmRelease/longhorn-system/longhorn
├── PriorityClass/longhorn-critical
├── ServiceAccount/longhorn-system/longhorn-service-account
├── ServiceAccount/longhorn-system/longhorn-ui-service-account
├── ServiceAccount/longhorn-system/longhorn-support-bundle
├── ConfigMap/longhorn-system/longhorn-default-resource
├── ConfigMap/longhorn-system/longhorn-default-setting
├── ConfigMap/longhorn-system/longhorn-storageclass
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backingimagedatasources.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backingimagemanagers.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backingimages.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backupbackingimages.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backups.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backuptargets.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/backupvolumes.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/engineimages.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/engines.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/instancemanagers.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/nodes.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/orphans.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/recurringjobs.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/replicas.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/settings.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/sharemanagers.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/snapshots.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/supportbundles.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/systembackups.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/systemrestores.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/volumeattachments.longhorn.io
├── CustomResourceDefinition/volumes.longhorn.io
├── ClusterRole/longhorn-role
├── ClusterRoleBinding/longhorn-bind
├── ClusterRoleBinding/longhorn-support-bundle
├── Service/longhorn-system/longhorn-backend
├── Service/longhorn-system/longhorn-frontend
├── Service/longhorn-system/longhorn-conversion-webhook
├── Service/longhorn-system/longhorn-admission-webhook
├── Service/longhorn-system/longhorn-recovery-backend
├── DaemonSet/longhorn-system/longhorn-manager
├── Deployment/longhorn-system/longhorn-driver-deployer
└── Deployment/longhorn-system/longhorn-ui
$ flux tree ks longhorn-config
Kustomization/flux-system/longhorn-config
└── Ingress/longhorn-system/longhorn-nginx
$ kubectl get storageclasses.storage.k8s.io
NAME PROVISIONER RECLAIMPOLICY VOLUMEBINDINGMODE ALLOWVOLUMEEXPANSION AGE
longhorn (default) driver.longhorn.io Delete Immediate true 2d9h
longhorn-static driver.longhorn.io Delete Immediate true 2d9hIf everything goes well, you should be able to reach the longhorn webui at longhorn.yourdomain.tld, and it should even be served using it’s own LE certificate.
Sources
- longhorn.io: Talos Linux Support
- hackmd.io: Install Longhorn on Talos Kubernetes
- calebcoffie.com: Part 3: Adding Longhorn for Persistent Storage on Our Talos-Powered Kubernetes Cluster
- kubernetes.io: Set up Kubernetes tools on your computer